Treatment Overview for Lyme disease
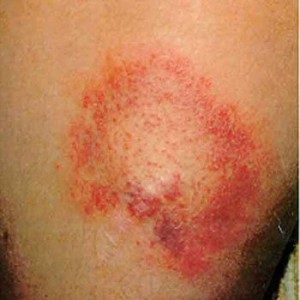
Lyme disease is a form of infection that spreads after being bitten by infection-ridden ticks that are carriers of Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium leading to bulls-eye type rashes, weariness, headaches, rigidity in neck, fever, muscular or joint aches and swell up. In case prompt treatment is not given complications that involve the cardiovascular, nervous system, joint and skin could imminently develop.
Lyme disease is generally effectually treated with a brief antibiotic course and often recommended in the advanced staging of the disease. Prescription of antibiotic medicines is based on the age, signs and staging of the disease and given via oral, jab or intravenously. The span of antibiotic treatment would vary in accordance to severity of the disease, signs experienced, and normally lasting lesser than four weeks.
Antibiotics Prescribed
Amoxicillin, cefotaxime or ceftriaxone sodium, erythromycin, penicillin, tetracycline hydrochloride, doxycycline hyclate, cefuroxime axetil.
Preliminary Staging Lyme disease Treatment
- Those eight years and above, the span of antibiotic course is dependent on the type of antibiotic and how severe the infection is.
- Doxycycline is contraindicated during pregnancy or kids below eight.
- Oral intake of amoxicillin is prescribed for below eight year old children. Other medicines like erythromycin could additionally be prescribed in case the kid is having allergic reactions to amoxicillin.
Advanced Staging Lyme disease Treatment
 In case of Lyme arthritis (Lyme disease induced joint inflammation that could keep relapsing), orally taken antibiotics are generally advised for some weeks. Intravenous administration of antibiotic is given in case oral antibiotics are showing no success.
In case of Lyme arthritis (Lyme disease induced joint inflammation that could keep relapsing), orally taken antibiotics are generally advised for some weeks. Intravenous administration of antibiotic is given in case oral antibiotics are showing no success.- Oral antibiotics are generally effectual in treatment of facial paralysis with no nervous system conditions.
- Intravenous antibiotics are administered in case of acute heart signs of Lyme disese or for nervous system conditions developing due to Lyme disease like Lyme meningitis.
Lyme disease treatment During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Women diagnosed with having early stages of Lyme disease generally are advised oral course of antibiotics for many weeks. Few physicians consider that expectant mothers having early Lyme disease must be administered intravenous antibiotics for preventing Lyme disease from permeating placental membrane of the growing fetus. However, there is dearth of evidence whether such treatment is required.
- Intravenous administration of antibiotics is prescribed among pregnant or breastfeeding women with advanced stages of Lyme disease.
Side Effects
- Feeling nauseous.
- Mild loose bowels.
- Having an allergic reaction.
- Vaginal, intestinal or oral thrush secondary yeast infection.
- Few undergoing Lyme disease treatment face short periods of headaches, muscular, joint pains and weariness continuing for protracted time periods following treatment. These would generally subside in six months and not needing additional treatment.
- Higher fever, increased pains or more reddish rashes could develop in the initial day following intake of antibiotics. Though not indicative of an allergic reaction, it could signal rapid death of the bacteria.
- A large-scaled study indicated that those taking erythromycin alongside other commonly used medications like some antifungal medications, antidepressants and particular drugs inhibiting some liver enzyme like some calcium channel blockers could increase their chances of abrupt cardiac death.
Efficacy of Antibiotics Course
A number of symptoms would last for many weeks subsequent to treatment. However, this does not translate to the fact that the antibiotics were not effective or that further antibiotics course is required.
- Early Lyme disease generally improves following intake of oral course of amoxicillin or doxycycline for about thirty days.
- Doxycycline must ideally be consumed with plentiful fluid intake and preferably not when one lies down or just prior to sleep times. It must not be given to expectant mothers or those having allergic reactions to tetracycline.
- For all those offered intravenous administration of antibiotics, blood analysis would be done every week for checking any plummet in white blood cell count that often could arise and make it trickier to combat infection.



