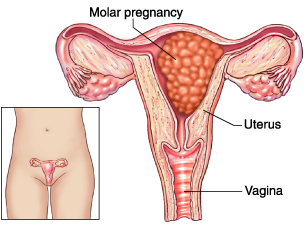
Molar Pregnancy (Hydatidiform Mole)
Molar pregnancy is a typical accretion or growth forming within the uterine region at the onset of gestation. It is a form of GTD or gestational trophoblastic disease (an assemblage of irregularities wherein tumor growths occur within the uterine region starting in tissue which would usually develop into placenta).
 Causes, Risk Factors & Prevalence
Causes, Risk Factors & Prevalence
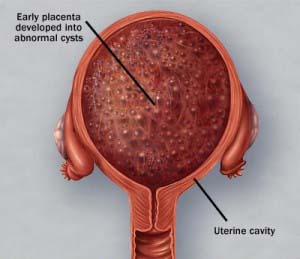
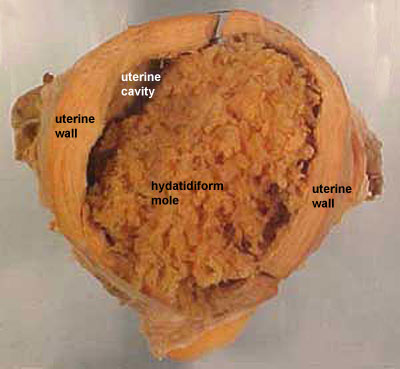
Molar pregnancy arises due to overproduction of the tissues which were intended to become the placenta (organ forming during gestation for feeding the fetus). In such a situation, the tissues would be developing into an unusual growth known as mass. Molar pregnancy occurs in duo forms, namely, complete molar pregnancy (presence of irregular placenta in the absence of fetus) & partial molar pregnancy (presence of irregular placenta & some fetal growth). These duo types are the result of fertilization issues for which the precise reason is unknown. But, a dietetic intake less in proteins, vitamin A, & animal fats might don a part.
Symptoms
- Irregular uterine growth.
 Excess development in around fifty percent of the cases.
Excess development in around fifty percent of the cases.- Lesser than anticipated development in around 1/3rd of the cases.
- Feeling nauseous, puking which might be so acute that the woman might need to be hospitalized.
- Bleeding from vagina in the initial three months of gestation.
- Signs & symptoms of hyperthyroid condition
- Intolerant to heat.
- Looseness in bowels.
- Swift cardiac rate.
- Restiveness, edginess.
- Hand quivering.
- Inexplicable weight reduction.
- Signs analogous to preeclampsia which takes place in the initial trimester or earlier part of middle trimester – it is an indication of a molar pregnancy in most occasions since preeclampsia is rather atypical in such a preliminary stage of normal gestation.
- Hypertension.
- Swollen ankle, leg & foot areas.
 Diagnosis & Testing
Diagnosis & Testing
A pelvic exam might reveal indications akin to regular gestation; however the uterine size might not be normal & fetal heart beat amiss. There might be some extent of blood loss from the vagina.
Ultrasound scan would reveal an abnormally occurring placenta in the presence or absence of fetal growth.
Testing conducted would comprise of:
- CBC (complete blood count).
- X-ray done of the chest.
- Tests for checking kidneys & liver functioning.
- Tests to check blood coagulation.
- CAT or magnetic resonance imaging scanning of the abdominal region.
- HCG blood test.
Therapy
- In case molar pregnancy is doubted then the physician might perform a Dilatation and curettage (D & C) method wherein removal of inner uterine matter is done after cervical dilatation.
- Hysterectomy (operative removal of uterus) might be a choice for elder females who don’t intend to bear children anymore.
Post-therapy, follow-up of serum HCG levels would be done. It is crucial to not get pregnant & deploy a dependable birth control for six months to a year post-therapy done for molar pregnancy. Doing so permits precise testing to ascertain that the irregular tissue doesn’t recur. Females conceiving soon following a molar pregnancy carry a higher risk for experiencing it yet again.
Outlook
Over eighty percent cases of hydatidiform mole are benignant and results post-therapy are generally quite favourable. Such women need to be followed up closely by their doctors. Post-therapy, women must be using an effectual birth control method for a minimum of six months to a year’s time to avoid getting pregnant.
In particular situations, a hydatidiform mole might turn into an invasive one which could show deep-set growth inside the wall of the uterus & causal to blood loss or several complications.
In several scenarios, hydatidiform moles might form into choriocarcinomas, a swift-spreading malignant type of GTD.
Complications
Lung-related conditions might arise following a dilatation & curettage procedure when the uterus is more than sixteen weeks of gestation. Thyroid conditions & preeclampsia are some complications linked to surgical procedure for removal of molar pregnancy.



