Alzheimers Stages – Experts Developed 7-Stage Framework
 Specialists have set up ‘stages’ for describing the manner in which an individual’s capabilities alter from usual functioning all through the Alzheimers stages.
Specialists have set up ‘stages’ for describing the manner in which an individual’s capabilities alter from usual functioning all through the Alzheimers stages.
It is crucial to bear in mind that stages are a broad guide & symptoms varying significantly across sufferers. Not every Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patient would be experiencing the analogous symptoms or be progressing at the analogous pace.
The 7-stage outline is devised on the basis of a system created by Doctor B. Reisberg, Director NYU School of Medicine, Silberstein Aging & Dementia Research Center.
Alzheimers Stages
Stage 1 – Regular functioning
The AD patient experiences no weakening or disablement. The individual wouldn’t be experiencing any recollection issues. When interviewed by medical experts there’s no proof of any symptoms.
Stage 2 – Quite Mild Cognitive Declension (might be usual aging-linked alterations or most preliminary AD signs)
The individual might sense himself/ herself experiencing memory slips – not remembering known phrases or where daily use items are located. However, any symptoms couldn’t be identified in the course of a medical exam or by buddies, kin or co-employees.
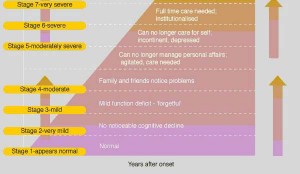 Stage 3 – Mild-ranging cognitive declivity (early staging AD diagnosis in few, though not all symptomatic people)
Stage 3 – Mild-ranging cognitive declivity (early staging AD diagnosis in few, though not all symptomatic people)
Kin, chums or co-employees start noticing something off-beam in the person. In the course of a comprehensive medical interviewing session, physicians might spot issues related to concentration or recollection. Prevalent problems typical to this stage comprise of:
- Apparent difficulties surfacing with the correct words or names.
- Problems faced trying to remember name on introduction to individuals for the first time.
- Experiencing apparently more hurdles doing duties in social or job situations. Not remembering something which one lately saw.
- The person loses or misplaces a costly item.
- Increased issues faced when the person plans or organizes.
Stage 4 – Moderately Occurring Cognitive Declivity (Mild or preliminary staging of AD)
At this juncture, a meticulously conducted medical interviewing would clearly spot issues in many quarters:
- Forgetful about latest happenings.
- Impeded capability of performing mental arithmetical challenges – like to count back from a hundred by 6s.
- Increasing problems faced when doing intricate jobs like to plan a meal for a guest-list, bill payment or monetary management.
- Forgetful regarding one’s own past.
- Moodiness or withdrawing into a shell, particularly in social or mental tricky scenarios.
Stage 5 – Fairly acute cognitive declivity (moderate/ middle staging AD)
Memory or thought process gaps are apparent & people start needing assistance in daily tasks. During such a staging, AD patients might:
- Be incapable of recalling their residence address or contact numbers or from which institution they did their schooling or graduation.
- Confusion regarding where he/she is or which day it is.
- Problems with lesser tricky mental maths like to count back from forty by subtraction of fours or from twenty back by twos.
- Requires assistance to choose apt clothes for the weather or occasions.
- Yet remembering important details regarding self & kin members.
- Yet needing no help to eat or use the loo.
Stage 6 – Acute Cognitive Declivity (fairly acute or middle staging AD)
Continual worsening of memory, personality alterations might occur & people needing major assistance with everyday chores. In such staging, people might:
- Begin losing consciousness of fresh experiences and surrounding.
- Remembering his/her name, though facing difficulties with personal past.
- Tell apart known from unknown face though having problems recollecting the name of partner or caretaker.
- Requires assistance to dress appropriately, & might commit blunders when not supervised like donning night clothing on top of morning wear clothing or footwear on the wrong foot.
- Experiences key alterations in slumber patterns – sleeps in the daytime & restlessness during nights.
- Requires assistance to handle details of loo use – for instance, flush the chair, wipe or dispose the tissue aptly.
- Experiences more regular problems to control bowel or bladder.
- Experiences key character & behavioural alterations inclusive of becoming suspicious, delusional (like he/ she believes that his/ her caretaker is a phoney, recurring behaviours like wring hands or shred tissues.
- Tendency of wandering or becoming lost.
Stage 7 – Very acute cognitive declivity (acute/ late staging AD)
During the last staging of AD, people become incapable of responding to their surroundings, conducting conversations & ultimately controlling movements. The person might yet be capable of saying word or expressions.
During this staging, people require assistance with nearly all everyday personal care like to eat or use the loo. He/ she might even become incapable of smiling, sitting or holding head up independently and suffer from irregular reflexes, muscular rigidity & ingestion impairment.



